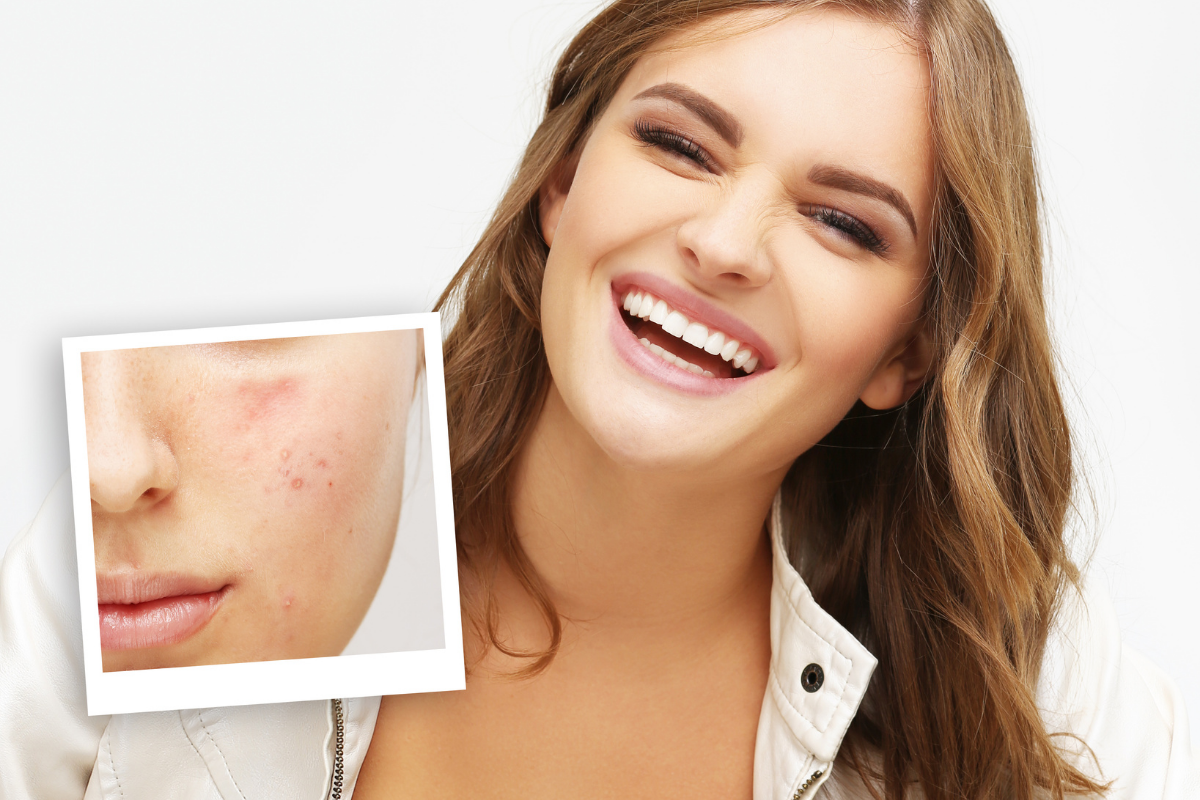
A chronic skin disease occurs when the excretory function of the sebaceous glands or hair follicles is impaired. A typical sign of exacerbation is the appearance of acne, pustules and comedones on the face and body, which is accompanied by increased secretion of sebaceous glands. There are many reasons for the occurrence and development of acne, associated with hormonal imbalance, infections, and frequent stress.
Acne is the most common reason for consulting a dermatologist. The disease in various stages and degrees regularly manifests itself in 70-80% of people. The peak of exacerbation falls on the period from 13 to 20 years and is associated with hormonal imbalance, its instability. The problem persists up to 30 years in 25-45% of people, and is disturbed by rare relapses in about 15% of patients after 40 years.
In most patients, acne rash is concentrated in the face, upper back and chest. Without proper diagnosis and timely treatment, it is difficult to avoid scarring of soft tissues: scars, bumpy irregularities remain for a long time, requiring correction (laser resurfacing, dermabrasion, etc.). Severe acne can lead to nervous disorders, mental problems. The patient becomes withdrawn, irritable, and may fall into depression.
What does acne look like?
The disease occurs individually in each person. The manifestation depends on age, gender, the presence of chronic pathologies of the endocrine and digestive systems. Characteristic rashes of various sizes appear on the skin of the face and body. They are accompanied by enlarged pores, comedones, redness, pustular rashes.
Acne has a variety of manifestations. The main elements of the rash: comedones, nodular pustules, cystic formations. Depending on the severity, they can be single, can cover the entire forehead, face, back or shoulders. Most often localized in areas with the largest number of sebaceous glands.
Types of acne
In cosmetology and dermatology, the general name "acne" is used. It combines several types of acne. They differ in shape, appearance, size and number of rashes, so treatment is selected depending on the characteristics of the rash. Knowledge of the detailed classification allows you to correctly prescribe medications according to the principle of action.
Blackheads (comedones)
In the initial or middle stage, the pores are clogged with sebum. They become compacted, forming a hard plug of white or yellow color. Through narrow ducts, they take the form of an oblong rod. A blackhead occurs when cells and fats are oxidized under the influence of oxygen. They can turn into whiteheads or large subcutaneous fat deposits.
Purulent acne
When pathogenic bacteria are activated in the hair follicle, inflammation occurs. The accumulation of exudate occurs when the immune system tries to contain the process. The contents remain in the duct, which requires appropriate care and removal by a specialist. When trying to squeeze it out yourself, rough scars with a diameter of up to 5 mm or more often remain.
Papules
In acute inflammation of large comedones, a pink or red lump appears. It rises above the skin, can cause pain, burning or itching. When merged, it reaches 1 cm in diameter, provokes swelling and puffiness. Diagnosed with moderate and severe acne, can be on the back, chest and buttocks.
Pustules
One of the subspecies of the inflammatory process of the hair or sebaceous duct. Most of the pus accumulates deep in the dermis, so a large "bump", swelling and red compaction appear. When palpated, the patient feels a hard ball covered with a layer of skin. After opening, dark spots remain due to impaired pigmentation during the production of melanin.
Cysts
With total damage to the sebaceous gland and weak immunity, cysts form on the body. They reach a size of 1 cm, are dense to the touch. They contain a large amount of pus, can cause unpleasant pulsation, discomfort and even an increase in lymph nodes. They are the most problematic and severe form of acne.
Knots or nodules
They lie deep in the dermis, affecting the mouth of the duct from the inside. The accumulation of inflammatory exudate has no outlet through a tight plug, so it affects the surrounding skin areas. It is characterized by severe pain, 1-2 cm in diameter, and the appearance of swelling. It can cause fever, weakness, and general deterioration of well-being.
Signs and symptoms
In most patients, dermatologists diagnose local manifestations of acne in the form of polymorphic elements of the same type. At the initial stage, black comedones appear more often, the appearance of the skin in the affected area worsens. After exacerbation, pustular and cystic formations appear. They increase in diameter, rise above the surface of the skin.
The main symptoms that indicate the development of acne:
• pores expand in the forehead, nose, and chin area;
• red rashes are itchy and can be painful;
• a feeling of tightness arises;
• noticeable shine appears 1-2 hours after washing;
• the skin acquires a dull hue and becomes uneven.
With secondary infection, an inflammatory process occurs, suppuration increases, cysts are formed that are dense to the touch. In severe cases, cicatricial changes begin in the dermis. Rough scars from connective tissue remain at the site of the rashes.
Unlike furunculosis and other skin inflammations, acne is usually not accompanied by an increase in body temperature. The patient usually does not have an increase in lymph nodes. The process of the appearance of new rashes can occur continuously for several months or even years. At the same time, working capacity is maintained, if physical exertion is not prohibited.
Scars
After a long inflammatory process, unsightly scars may remain on the skin. They are formed when the integrity of the skin is disrupted and skin cells malfunction. This complication is observed in 90% of patients with severe acne.
The main reason for the appearance of scars after acne is an excess of collagen fiber deposits in the place of violation of the integrity of the skin after the healing of a cyst or deep pustule. The structure of the duct changes, it is compacted along its entire length to the deep layer of the dermis. Round or oval scars appear on the surface, reaching a diameter of 0.5 cm, uneven tuberosity is formed.
Three types of scars can form after acne. Men, patients with coarse skin of a combination or oily type, more often develop keloid scars. They appear on the site of previous rashes, are round in shape, extend beyond the edges of the healing rashes. Hypertrophic scars do not extend beyond the boundaries of previous rashes. Atrophic scars are areas of skin depression in places of previous rashes.
Pigmentation
With prolonged acne, the amount of melanin in the upper layer of the epidermis may change. This pigment is responsible for the natural shade of the skin. Its level increases at the site of inflammation after healing, leaving dark spots (pigmentation), sometimes resembling freckles.
Pigmentation is a complication that occurs when the production of melanin in damaged cells is disrupted. The problem is more often diagnosed in people with dark skin, aggravated by frequent exposure to direct sunlight. It gradually disappears after the use of special cosmetics or procedures. Therefore, during the period of exacerbation, dermatologists recommend additionally using creams with sunscreen filters of at least SPF 15.
Stages of acne development
An unsightly rash appears when several provoking factors combine. In dermatology, several stages are distinguished depending on the symptoms. They differ in the nature of the course, the number of rashes, the presence of complications, and the area of skin damage.
There are the following stages of acne:
• Mild, or initial. Several small rashes, redness of small diameter appear on the face. Their number does not exceed 10, papules are localized in places of increased secretion. There is no discomfort, pain or abscesses. Comedones are practically invisible, easily hidden under a layer of decorative cosmetics.
• Average. The number of rashes increases to 20, inflammation becomes pronounced, accompanied by hyperthermia of the skin, the formation of abscesses. Black dots cover the wings of the nose, chin and cheeks. Oily shine quickly appears after washing or applying makeup. In the acute stage, bluish spots often remain after removing acne due to impaired microcirculation.
• Severe. There are at least 40 lesions of various sizes and diameters on the face and various parts of the body, with purulent discharge. Large papules and nodules with exudate are formed, and the first scars are observed.
Some international classifications provide for an extremely severe stage of acne with a neglected skin condition. Acne is in a state of suppuration, leaving open wounds after opening. This creates conditions for secondary infection with bacterial or fungal infections, which complicate the course of acne. The period of the lesion is characterized by a depressed state, the development of psychological discomfort, and isolation.
Etiology and pathogenesis
In dermatology, acne is a polyetiological disease. This means that its formation is influenced to varying degrees by several external and internal factors. In 75-80% of the studied cases, the problem is present in the history of one of the parents, is hereditary, the predisposition is transmitted at the genetic level, like many skin pathologies.
During inheritance, the body receives information from several generations, distant relatives. This explains the difference in symptoms in children in the same family, the peculiarities of the course. The psychological situation, chronic pathologies of the digestive, endocrine, vascular systems are important.
Acne classification
In domestic dermatology, a classification system is used that provides a simplified description of the stages and degree of acne development. It serves to select the optimal and most effective treatment regimen.
The classification involves division into the following forms:
• normal, or mild , with isolated rashes, minimal manifestation of acne, discomfort, and no irritation.
• comedonal , or relatively mild form of acne, with an increased number of black comedones that create the effect of skin contamination.
• papulopustular , or moderate, with acne without suppuration. There is redness and other signs of inflammation.
• nodular-cystic , or severe, with a large area of damage. The rash is characterized by a large number of pustules and papules, comedones are large and raised above the surface.
There is no strict scale of acne that allows a doctor to accurately describe the problem. The average degree of damage is considered to be when comedones appear on the face and body. Severe is the process with the formation of large nodular formations containing inflammatory exudate.
Newborn acne
It occurs in 25% of children under one year of age, forms in the first weeks after birth. The rash is represented by small white dots that cover the nose, cheeks, lower eyelid, nasolabial folds. The problem directly depends on the level of sex hormones in the blood of the newborn. They are transmitted during intrauterine development from the mother, increase when the baby's adrenal glands are working.
In the absence of other risk factors, this type of acne does not require treatment. During breastfeeding, the hormonal background gradually normalizes, the composition of the blood changes. The skin clears up within a few weeks. A possible complication is the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, which can lead to severe suppuration and scarring of the tissues.
Juvenile (teenage) acne
Occur in 80-90% of children aged 12 years and older, later appearing in boys. In the event of severe clinical acne, mandatory treatment under the supervision of a dermatologist, correction of nutrition, hygiene is required. Acne is characterized by frequent relapses with an increase in the level of propionic bacteria in the sebaceous gland.
Characteristic signs of youthful acne:
- open black dots up to 1 mm in diameter;
- coverage in the T-zone;
- the presence of white nodules;
- redness of the epidermis.
Often, exacerbation is accompanied by the formation of large nodes that cause severe pain. The cavities are filled with purulent contents, the skin around becomes red, swollen, itchy, and hot to the touch. They can leave deep wounds, which after healing turn into large rough scars. In difficult situations, damage to the sweat glands occurs, furunculosis joins.
Adult acne
The causes of the disease in patients over 30 years of age are more diverse, often associated with hidden processes in internal organs and systems. Acne has a chronic form. Relapses are provoked by hypothermia, stressful situations, lack of sleep and dehydration.
Common forms of acne in adults include:
• Late acne in women due to menstrual cycle instability, menopause, and gynecological problems.
• Inverse acne localized in the perineum and armpits with damage to the sweat glands.
• Bodybuilding acne, when abusing synthetic hormones based on steroids and androgens when building muscle mass.
• Spherical acne, which indicates the development of polycystic ovary syndrome in girls. It is often accompanied and complicated by seborrhea.
In adults, a closed rash with skin lumpiness prevails. Unlike juvenile acne, nodules form in the deep layer, cover the chin, provoke dryness and peeling. Regeneration slows down, the color becomes duller, and fine wrinkles appear.
Adult acne often occurs due to professional activities. Workers in the chemical industry and agriculture, who constantly use chemicals, harmful pesticides, petroleum products, bromine, and tar, are prone to this problem.
Classification by age
When diagnosing acne, the patient's age is of great importance. At a young age, in 90% of cases, the cause is a change and sharp fluctuations in the hormonal background. The main risk factor is jumps in the production of androgens and testosterone, which can significantly exceed the norm and provoke complications. A distinctive feature of a youthful rash is its localization on the face, wings of the nose, forehead, a large number of comedones and enlarged pores.
In adult acne, the hormonal factor is enhanced in the presence of damage to the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, severe pathology of the reproductive system. Exacerbation occurs more often during premenstrual syndrome, decreases after menstruation. The rash covers the lower part of the face, a large number of inflammatory papules, less often purulent cysts are present.
Causes of acne
The basis of the development of the inflammatory process is a hereditary increased function of the sebaceous glands with a violation of the natural release of their secretion to the skin surface. It clogs the follicles, remains inside the mouth, and provokes a sharp growth of bacteria. Many years of clinical studies have proven that acne can be associated with exogenous and endogenous factors.
In some situations, patients have a combination of several factors of different types. Their manifestation is influenced by age, a decrease in immune defense, and a decrease in intestinal function. In each case, a comprehensive diagnosis is performed. It is aimed at identifying key factors that require correction and treatment.
Exogenous causes
Several external factors affect the health and condition of the skin. They lead to disruption of microcirculation processes, activate glands, reduce the protective barrier. They increase the duration of acne, the severity of the course, and the number of complications.
Many exogenous causes lead to the rapid growth of propionic bacteria, change the external microflora of the skin, making it more susceptible to irritants. A large group of risk factors is actively studied in diagnostics. The key to effective treatment is its complete elimination.
Makeup
Some skin care products and decorative series for applying makeup contain components that can increase the blockage of pores with sebum plugs. Experts distinguish them into the group of “comedogenic products”. Active substances cover the skin with an invisible film, create a greenhouse effect. These include: soybean, coconut, almond oil, petrolatum and its derivatives, lanolin.
Clinical studies conducted in recent years do not recommend using cosmetics with sodium lauryl sulfate, squalene and oleic acid. If you have a problem, you should give preference to a series marked "non-comedogenic", carefully study the composition. If acne appears, makeup can worsen the situation: special cosmetic products with a therapeutic effect are allowed.
Hot and humid climate
People who travel to tropical countries often experience acne flare-ups. High temperatures, high humidity, and lots of sunlight stimulate the sebaceous glands. Trying to restore balance to the epidermis, more moisture comes to the surface, drying occurs, and a foundation is created for the growth of bacteria and microorganisms.
Working with toxins and chemicals
With constant contact with household and professional chemicals, particles settle on the skin, penetrate into the digestive tract. Intoxication develops, immunity decreases, some of the toxic compounds accumulate in the subcutaneous layer. Toxins from the inside worsen the condition of the skin, triggering a relapse of the inflammatory process.
When working with chemicals, acne manifestations are often complicated by an allergic reaction, inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Large and rough nodules appear on the face, the relief changes, and the general well-being may worsen. The rash covers the back, abdomen, and groin area. Treatment should begin with detoxification, eliminating the source of poisoning.
Constant mechanical impact on the skin, friction, microtrauma
When unsightly acne appears on the face, most patients self-medicate. With frequent and incorrect squeezing of comedones, bacteria penetrate the pores, a secondary infection occurs. It changes the turgor and external relief of the skin, leads to scarring. Clogged follicles produce more secretions, the problem progresses to a more complex stage.
Such a complication can be provoked by wearing a protective and medical mask that a person does not change every day. It occurs when rubbing with a scarf, wearing clothes made of synthetic fabric, and improper shaving. Microtraumas are an open gate for infection and the appearance of abscesses.
Improper skin care
A common external factor is a person's inability to properly cleanse the skin. With excessive cleanliness and frequent use of soap, shower gels, the natural protective layer is washed off from the epidermis. Trying to restore it, the glands increase the production of secretions, trying to restore the pH after bathing.
An equally urgent problem is the unnecessary use of antibacterial lotions and soaps. They gradually become addictive, reduce their effectiveness, and destroy beneficial microflora. In a normal state, bacteria are always present on the upper layer of the skin, which control the work of the glands and moisture, which suppress inflammation.
Demodecosis
The problem is associated with the activity of the skin mite of the genus Demodex. Penetrating into the dermis, it affects the upper layer, constantly moving, provoking burning, irritation, unbearable itching. Small localized foci with a nodular rash of red color appear on the body, redness and peeling may be observed. Pathogenic bacteria enter the open channels, inflammation begins.
Demodicosis is not directly the cause of acne, but it reduces local immunity, increases the risk of infection of the upper layer of the dermis. In combination with other factors, it triggers relapse, contributes to the spread of the process. Externally, rashes after a tick are identical to acne, so a comprehensive diagnosis using several methods is required.
Zinc deficiency
Doctors call one of the causes of acne a lack of zinc in the body. This trace element supports the immune system, inhibits the growth of bacterial microflora. It controls the level of secretions from the ducts, helps eliminate shine, and improves the quality of the skin.
According to dermatologists, exacerbation often occurs against the background of zinc deficiency. When it is included in the diet with the help of dietary supplements, it is possible to accelerate wound healing by 65% after removal of cysts and papules. The intensity of rashes, redness, and localization are reduced by 45%. The trace element is often used in specialized cosmetic products for external use.
Endogenous (internal) causes of acne
The condition of the skin depends on the coordinated work of the internal organs of a person. Failures and disorders reduce immunity, interfere with the absorption of zinc and other trace elements. Therefore, when diagnosing and identifying the causes of acne, the anamnesis is carefully studied, chronic and congenital pathologies of the digestive system, reproductive organs, tumor processes in the thyroid gland, adrenal glands are taken into account.
Testosterone and acne
Androgenic hormones are present in the body of any person, they affect the work of the sebaceous glands. When their level increases above normal, there is increased productivity of the sebaceous gland. The problem with diagnosis occurs in 80% of adolescents during puberty. It can be exacerbated by steroids, which are present in medications, contraceptives, food supplements used in sports training.
Premenstrual acne
In women, the main cause of inflammation is the activity of the sex hormones progesterone and estrogen, which are necessary for ovulation and conception. They increase sharply in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. Acne appears in the lower jaw and cheeks, can be localized on the upper chest. The problem can worsen sharply in the first trimester of pregnancy, completely disappears after menopause.
"Hormonal" inflammation
In many diseases of the endocrine system, the balance of hormones in the blood is disturbed. Pathological changes in the structure of the pituitary gland or adrenal glands lead to sharp fluctuations in indicators, exacerbation of chronic problems. In diffuse or thyroid goiter, rashes indicate the need to consult an endocrinologist.
Hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis can develop when the stratum corneum of the dermis grows. It progresses under the influence of a number of reasons: hormonal changes, lack of vitamin A, application of dangerous chemical compounds to the skin or mechanical factors (rubbing with glasses, a scarf, pressure from a helmet). The thickened stratum corneum, together with altered skin secretions, closes the pores and becomes a favorable environment for the development of the pathological process.
Gastrointestinal tract diseases
The features of the daily diet directly affect the condition of the skin. With pathologies of the digestive system, many nutrients and vitamins are not absorbed properly. Toxins and fats can disrupt the work of the sebaceous glands, increasing their activity.
The main risk factors are any form of gastritis, colitis, dysbacteriosis. With these pathologies, acne is observed in every second patient, regardless of age and gender. Localization sites are the forehead, bridge of the nose, cheeks and corners of the lips. By improving the digestive process, 70% of patients manage to reduce the intensity of acne rashes and achieve a positive effect.
Individual microflora
Each person’s skin has its own microflora, the main part of which is Propionibacterium. With healthy immunity, the body controls their growth, suppressing outbreaks on its own. If the balance is disturbed, acne flare-ups occur. Among the possible factors are improper care, taking antibiotics, colds, hypothermia or vitamin deficiency.
Stressful situations
With a constant state of insomnia and anxiety, the level of stress hormones, androgens and testosterone increases in the body. This provokes a change in the background, basic processes and metabolism. Acceleration of metabolic processes during stress triggers the work of the glands, provokes negative changes, and is reflected in the condition of the skin. Seborrhea, dermatitis and psoriasis are exacerbated, and the growth of pathogenic microflora is enhanced.
Genetic cause
An important risk factor is hereditary predisposition to acne. In 80% of patients, when collecting anamnesis, it is revealed that the pathology was in the parents, close relatives. Doctors associate it with defects in several genes that are inherited in the family. But the nature of the course depends on the environment, stress level, gender and age of the person.
Diet
An internal factor is a diet high in glycemic index foods. Some adult patients are diagnosed with lactose intolerance or other components, so acne occurs after eating milk, yeast bread or sweets. In any case, keeping a food diary is necessary to help identify irritants.
Infections
Among the pathogenic microorganisms that can provoke the development of acne are anaerobic bacteria Propionibacterium acnes, which are normally found deep in the sebaceous glands and sebaceous hair follicle. Some strains get on the skin with dirty hands, adapt, penetrate into microcracks or cuts after shaving. They feed on sebum secretions, reduce immunity, and stimulate the formation of abscesses.
Immune system dysfunction
In each case, the symptoms of acne are individual. With strong immunity, the body manages to suppress the growth of microflora, so the disease passes in a mild stage. Only black dots appear on the skin, which can be easily removed without consequences. With weak protection, mild inflammation quickly develops into a severe stage, requiring the use of medications.
Pathophysiology
When studying the mechanism of acne formation, it was found that the main cause is the blockage of the exit of the sebaceous secretion from the mouth of the follicle. The body begins to produce it in large quantities when the hormonal background is disturbed, and hyperkeratosis does not allow the sebaceous secretion to leave the sebaceous gland and this creates the prerequisites for infection. The work of the sebaceous-hair apparatus changes, which cannot cope with the volume of sebum.
After the mouth is blocked, a dense plug of sebum, skin particles, and exfoliated epidermal cells forms. The area is additionally covered with a film of fatty deposits, blocking the access of oxygen. The pigment melanin begins to oxidize, the shade of the pore changes to black. If a thin layer of epidermis actively grows on top, a closed comedone is formed - milium.
The main hormone that controls the process of producing skin secretions is dihydrotestosterone. In women, the hormonal background is more influenced by androgens, which are produced by the adrenal glands. Their level reaches a peak between the ages of 12 and 15. In combination with the activity of pathogenic microflora on the surface of the skin, a reaction is triggered that provokes increased production of acne.
A large number of blackheads that appear simultaneously on the nose or chin is associated with the body's protective reaction. In response to the blockage of the pore, an immune response is formed: macrophages, neutrophils and other blood cells are sent to the inflammatory focus, which mix with the fatty secretion.
The process progresses rapidly over several days. The immune system additionally directs protective proteins, trying to convert the fat secretions into lipase enzymes. They stimulate the production of the antimicrobial component cathelicidin. This only intensifies the inflammation, requiring systemic treatment.
Diagnostics
If inflammation appears on the face or body, it is necessary to consult a dermatologist. Rashes at the initial stage should be diagnosed to exclude hidden autoimmune pathologies of internal organs, allergies, poisoning. In addition to a visual examination of the patient, the doctor conducts the following examinations:
• collection of family history to study genetic heredity;
• studies possible side effects of drugs taken for chronic pathologies;
• conducts general clinical tests for the level of basic hormones (androgens, testosterone);
• scraping from the skin;
• refers to a gynecologist or endocrinologist.
In the diagnostic process, doctors use international classification systems that help to understand the severity of the course. The most common are the Cook, Leeds and CASS scales. Additionally, questionnaires are used to understand the peculiarities of nutrition, hygiene, and increase the risk of rashes and relapse.
In most cases, a dermatologist makes a diagnosis, taking into account the hormonal sensitivity of acne. The main risk factors are age under 30, premenstrual syndrome, red lumps in the lower part of the face. Women are recommended to have an ultrasound of the pelvic organs and adrenal glands, which produce the main sex hormones.
Differential diagnosis
In some cases, acne can be easily confused with other pathologies in the body. Ordinary papules can mask an exacerbation of keratosis, which occurs when the hair follicles on the body become inflamed. Similar symptoms often resemble flat warts, a severe form of rosacea.
The main symptom that allows you to correctly diagnose the problem is the presence of blackheads, or comedones, on the skin. They accompany cystic, pustular and papular formations, indicating a violation of the production of skin secretions. Their presence allows you to exclude a food allergic reaction and intoxication after medications, chemicals, low-quality cosmetics.
Acne treatment
To obtain the effect, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive therapy under the supervision of a dermatologist. It is selected individually after comprehensive tests and taking anamnesis, aimed at eliminating existing defects. It is necessary to reduce the manifestations of acne, cosmetic problems, and normalize the secretion of sebum.
In moderate and severe forms, several methods are used. They include drug treatment with drugs, correction of nutrition, hormonal background, change of daily hygiene rules. Methods of eliminating defects (laser therapy, scrubbing, cryotherapy with nitrogen) are necessarily selected.
Comprehensive therapy
At the initial stage, it is recommended to visit a cosmetologist. He examines the condition of the skin, gives recommendations for home care. Special cosmetics from medical series help reduce the activity of the glands. They contain zinc, acids, vitamins, restore the production of fat to normal levels.
Combination therapy includes:
• Elimination of hormonal imbalance in case of menstrual cycle disorders, thyrotoxicosis, thyroid or uterine tumors.
• Taking drugs that restore intestinal microflora in case of dysbacteriosis, after intoxication, antibiotic therapy.
• Treatment of latent infections, inflammatory processes of the respiratory system, digestive system, liver, and pancreas.
In therapy, a combination of external and internal drugs, vitamin complexes, keratolytics is recommended. Given the peculiarities of skin regeneration, the effect may appear only after 7-21 days. It is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene, physical activity, and proper nutrition.
External preparations
For the treatment of acne, it is necessary to use external lotions, creams and gels. They contain medicinal components that penetrate the inflamed ducts, stimulate cleansing from the inside. They help to cope with infection, burning, normalize water balance and blood circulation, reduce the risk of pigmentation and scarring with active collagen production.
Effective groups of external preparations may contain active substances and components:
• Azelaic acid. Destroys blackheads, cleanses from excess sebum, protects against repeated inflammation in case of bacterial infection.
• Benzoyl peroxide. Antiseptic and keratolytic, whitens the skin with pigmentation, dissolves dead cells and plugs (for example, soap "Perolite" and "Perolite Plus")
• Tretinoin. Replaces vitamin A, helps cleanse the epidermis of open and closed comedones.
The components are relatively safe, rarely cause allergic reactions. They are included in the composition of gels for spot application, require long-term use for a cumulative effect. They are present in the medical cosmetics of many brands.
Antibiotics
If there is no effect, products containing antibiotics based on erythromycin, clindamycin (for example, soap "Perolait Plus") can be used. They are part of ointments for external use. But when canceled, the effect of addiction and relapse often occurs, so the doctor prescribes the regimen.
In inflammatory infections in the intestines and reproductive system, a course of antibiotic therapy based on doxycycline, tetracycline, minocycline is necessary. They inhibit the growth of microflora from the inside, normalize the condition, and allow you to continue therapy with external agents.
Antiandrogens
After tests that confirm hormonal disorders in women, drugs that suppress the production of androgens are prescribed. These are contraceptives for internal use. They differ in composition, hormone concentration, and estrogen profile. The average course of treatment takes up to 6 months.
Retinoids
Creams and gels contain a large amount of vitamin A, improve regeneration, open pores, cleanse the skin. Eliminate the accumulation of dead cells, plugs and blackheads. Help prevent pigmentation, restore elasticity and natural color ("Eleneon-A", "Adaklin", "Radevit", "Effezel").
In severe acne, topical retinoids of the 3rd generation are used. These are synthetic analogues of vitamin A, which differ in the principle of action on the skin ("Eleneon-N", "Retinal", "Tretinol", "Adapalene"). They are effective in the appearance of scarring, surface changes and tuberosity. In severe acne, a course of systemic retinoids based on isotretinoin is prescribed inside ("Eleneon Plus", "Eleneon Max", "Roaccutane").
Preparations with sulfur and salicylic acid
Inexpensive and effective preparations for external use, produced on the basis of natural sulfur and salicylic acid. They have an antimicrobial effect, eliminate inflammation, help reduce the number of rashes. They are used as a supplement to complex therapy (for example, Glycolite foam).
Ointments as a topical dosage form and topical preparations with a hormonal component are not recommended for the treatment of acne. Synthetic glucocorticoids for 1-2 weeks can give a positive effect, but at the same time they increase the activity of the adrenal glands, androgens are released into the blood, inflammation enters the active stage, and they also increase microbial inflammation.
Intensive acne treatment
In severe cases, modern methods help to avoid scarring. Deep cleansing, removal of cysts and papules are actively used in cosmetology.
The most effective methods for acne:
• removal of acne and papules in the clinic using spot laser therapy;
• deep cleansing with chemical peeling (used in mild cases to remove closed and open comedones without purulent eruptions);
• chemical exfoliation of the top layer to eliminate pigmentation and scarring.
Before starting treatment, a course of external retinoids for 4 weeks is recommended. They trigger regeneration, accelerate recovery and healing. Drainage of inflamed foci helps to avoid complications, the formation of papular nodules, and furunculosis.
Cosmetology methods
Procedures in the remission stage can be supplemented with mesotherapy: a drug containing valuable amino acids, vitamins, trace elements, and retinoids is injected under the skin. The general condition of the skin with acne improves, and enlarged pores are reduced.
Care products are prescribed with great caution. They are ineffective in case of hormonal imbalance, aimed at nutrition and hydration, reducing oily sheen. Exfoliation with the use of abrasive substances can stimulate the production of skin secretions, increase the appearance of acne.
Questions and answers
Is acne treatment necessary?
In the absence of comprehensive therapy, a severe form of acne may develop, with disfigured scars in the future; the rash may spread to large areas of the body. This provokes psychological discomfort, neuroses, and problems with self-esteem. Scars often remain, changing the relief on the face and body, forming an aesthetic problem for a long time.
How long does it take for acne to go away?
Depending on the cause, treatment can take from 3 months to several years. The most problematic situations arise with diseases of the reproductive organs and pituitary tumors.
What happens if grade 2-3 acne is not treated?
The pathology must be treated with the help of a dermatologist, cosmetic procedures alone are not enough. In most patients with severe forms, irreversible changes occur in the structure of the skin: it is replaced by connective tissue with a high collagen content. Rough, disfiguring scars remain, requiring long-term and expensive treatment.
Skin care
If you have acne, it is better to consult a cosmetologist to determine your skin type. He will select special cosmetics, cleansers and masks for regular use at home. Preference should be given to series that do not provoke the formation of comedones.
Diet
When acne flares up, doctors recommend eliminating foods containing sugar, yeast, spicy seasonings, store-bought sauces, citrus fruits, and fatty meats from your diet. You should include more fresh vegetables, fruits, and grains that contain fiber, zinc, and vitamins A and E in your diet. Calculating the glycemic index of foods can help.
Prospects for acne treatment
Vulgar acne in adolescence disappears without a trace by the age of 20 in 80% of people. With regular use of care products, it is possible to maintain the smoothness of the skin. Longer and more complex therapy is required for adult acne with chronic or autoimmune pathologies.
Pregnancy
In the first trimester, a sharp change in hormonal levels provokes an exacerbation of acne. The problem often disappears a few months after childbirth. But without systematic external treatment, scars and pigmentation may remain. Therefore, the use of external preparations with sulfur, zinc, and cosmetic procedures is recommended.
Acne prevention
In chronic cases, it is difficult to avoid repeated exacerbations. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the prescribed diet, monitor the functioning of the digestive tract, and avoid prolonged constipation, flatulence, and dysbacteriosis. The main recommendations of dermatologists for the prevention of acne:
• Do not use aggressive ingredients to cleanse and tone the skin, do not get carried away with scrubs and peels if you have oily and combination skin type.
• Follow hygiene rules, take a shower in the morning and evening, change your towel and underwear.
• Do not remove acne yourself, do not open pustules, papules and cysts at home.
• Do not use hormonal ointments or antibiotics for prevention.
• Apply cosmetics depending on the season, skin type and condition, sunlight intensity, and outdoor air temperature.
• Carefully study the composition of care products before purchasing.
With acne, it is necessary to regularly visit a cosmetologist in the clinic. In sterile conditions, he cleans the pores, removes dense plugs. This reduces the likelihood of scarring, accelerates healing.